FOR SHARE - JULY SNAPSHOT - 20230629 Draft Data Products
Early draft
Please be aware that the Data Spaces Blueprint content shared in these pages are a very early draft published on 2023-07-01. The current draft is incomplete and the content might still change.
SAVE-THE-DATE 01-10/09/2023: We will welcome your feedbacks to future improve the Data Spaces Blueprint during the Public consultation that will open on September the 1st 2023 until September the 10th. Please mark these dates in your calendar and get ready!
Draft building block snippet: Data Products
Overview
Perceiving data as a product is a mindset change in organisations – start producing data with reuse in mind. This solves the root cause of many problems related to the traditional approaches where business processes generate data without designing it to be shared. Productised data can be easily consumed, even by users who did not initially have any connection to the source of this data. Data products are gaining widespread traction in enterprise data architectures within organisations.
From the business perspective, the data products in data spaces are basic units of use cases. A Data space is a shared infrastructure for one or more use cases. The cost of the infrastructure is shared by all participants of all use cases. The costs of implementing (and operating) individual use cases can be divided into infrastructure- and other costs. The data space as a shared infrastructure should reduce infrastructure costs for individual use cases.
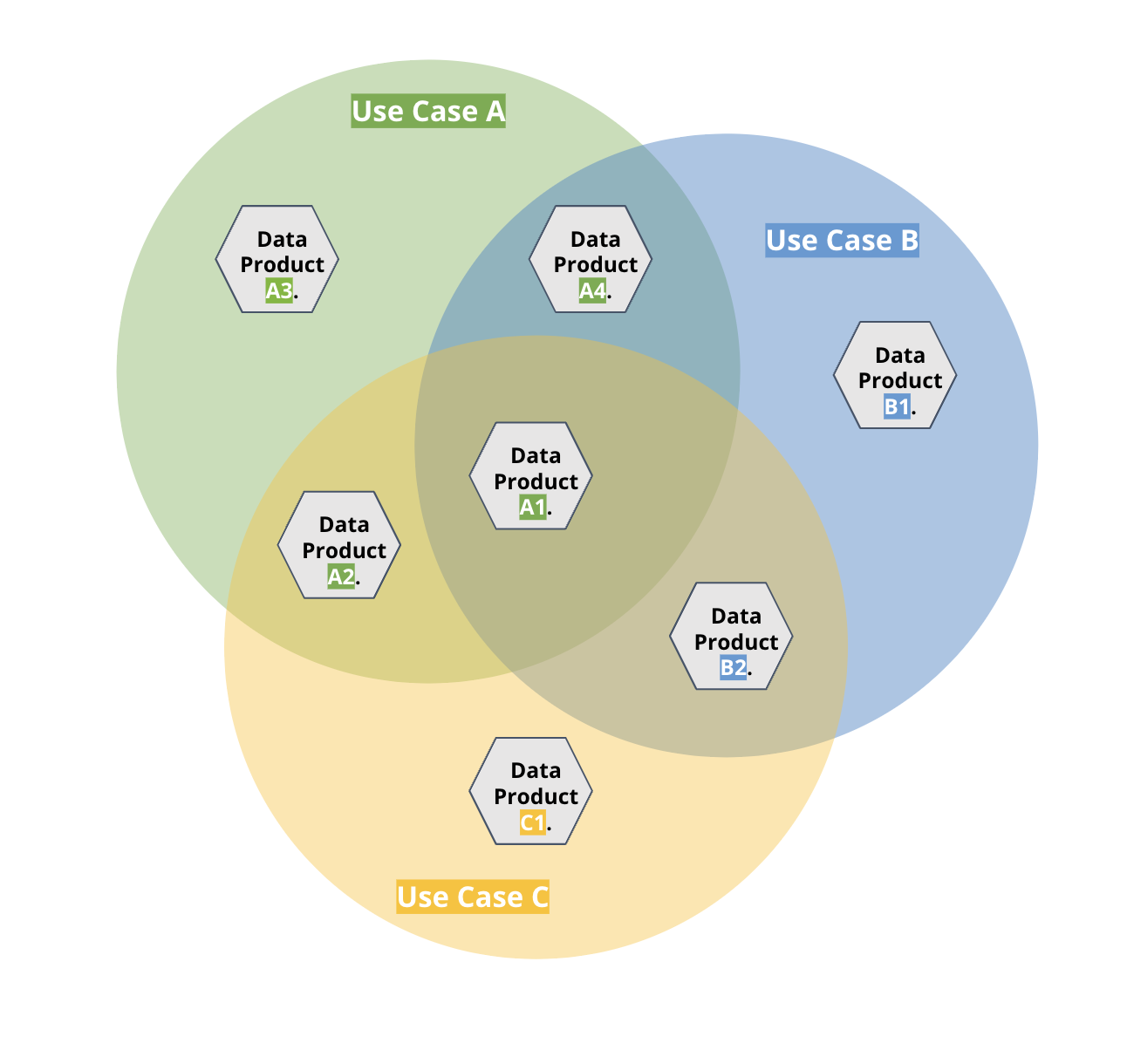
Data spaces can speed up the development of use cases in a given domain (e.g. logistics, tourism, skills, etc.) because the use cases often require the same data sources. If the data needed by a use case is productised (instead of tailored to the one use case only), then the data products can be directly used in the following use cases. Ready-made data products also facilitate the identification of new use cases and the development of innovations.
Figure 1: Visualisation of three related use cases that are partly relying on same data sources.
A data product building block aims to enable higher utilisation of trusted data by making its use easier for a diverse set of data receivers and data users. A data product is a business building block because it is a starting point for value creation.
From the demand perspective, data products can be seen as data containers directly usable for solving (potentially in combination with other data products) business problems in data space use cases. Consider the use case as providing the final service with business value for the end users. Then the data products are intermediate products necessary to produce the final service. In other words, the use cases make added value by utilising one or more data products as resources.
From the supply perspective, data products are the units of value creation for the data rights holders and -providers. Data products can be directly monetised or exchanged for benefits. Data rights holders can sovereignly define the precise scope and policies of the data products. However, there needs to be demand for the data product, or it will never be used. Therefore, creating data products should be started on the side of the data users to clarify the added value of the data product. From the supplier perspective, it is ideal if the same data product can be delivered with minimal changes to multiple use cases. Therefore it is important to be flexible on how the product will be packaged and to consider the commercial and technical requirements.
Key elements
Template processes to create data products and product offerings.
Key functions
Creation and prioritisation of data products and product offerings based on commercial and technical requirements.
Dependences and relationships
Data spaces conceptual model: Data product is a root element of the conceptual model.
Use case accelerator: synergetic use cases involve some of the same participants and the same data products.
Data description technical building block: The data product building block is complimentary and sets requirements to the technical building blocks under the value creation pillar (data description, product catalogue, product order, etc.)
Data governance: Data quality is an essential underlying factor for the utility of the data products.
Relevance for the data space
From the business perspective, the data products in data spaces are basic units of use cases. For data space participants data products provide a commercial framework that is inherently data centric.
From the governance perspective, data products embody the object of data governance by answering the question of "what data".
Technically, data products can be implemented with standards like the ODPS to be highly interoperable with different tools and systems that can manage data products.