RTSM Extract Mapping
Introduction
To ensure the extract data is correctly considered, the RTSM Extract Mapping page is used to align the extract data with the specification. In order to align the two data sets, ‘mapping’ is required. This mapping provides instruction to match values (e.g. visits, regions, dispensing units) in the extract with corresponding values in 4C Supply® during the loading process. All mappable values are sorted into ten tabs on this page.
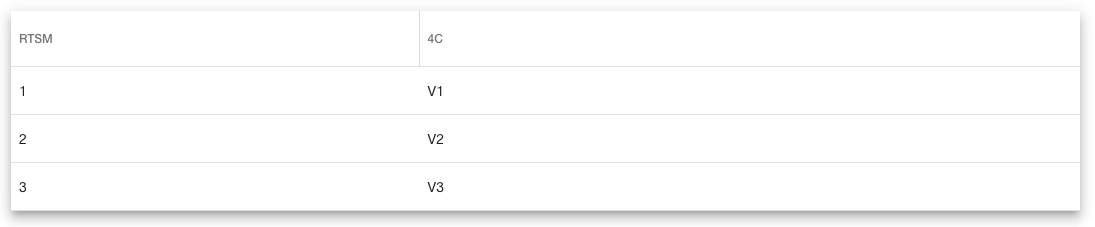
Example of RTSM visits (left) mapped to visits in a 4C specification (right)
The selectable values available in each tab of the RTSM Extract Mapping page are extracted from the most recent interpretation of the open scenario.
Changes made to mapping will be applied to the extract loads that follow. It is necessary to reload an extract in order to apply mapping updates.
Mapping is scenario-specific. If two scenarios use distinct values, e.g., different cohorts names, the mapping screen will reflect this.
4C Supply will attempt to map unmapped values (see Automatic Mapping below) - the system will match unmapped values to corresponding values in the 4C Supply® scenario specification if they are similarly named. If the system cannot make a connection, the value will be left unmapped and an error message on the RTSM Extract Loader will highlight the discrepancy. The aim of mapping is to resolve any warnings or errors that are not acceptable.
The mapping must be reviewed and updated to ensure that the extract data is correctly considered in the forecast. This may also require updates to the specification to bring it into better alignment with the extract data. If changes are made to the specification they must be saved and re-interpreted before they can be mapped.
Specification Alignment with the Extract
Whatever data is present in the extract should align with the specification in 4C Supply in order for it to be used. For example:
If the 4C specification introduces dose levels for all patients at Visit 3, then the system will expect to see dose-level data included in each patient’s Visit 3 record.
Conversely, if the extract data contains information about dose level in patient records but the specification does not include dose level information, it must be added to the 4C specification to enable the system to correctly process the patient data.
Mapping Interface
The mapping process requires users to match 4C Specification values to RTSM Extract values. The RTSM Extract values are divided into ten tabs:
Site Groups
Patient Visits
Depots
Regions
Kit Types
Treatment Arms
Cohorts
Titration Levels
Patient Statuses
Kit Statuses
RTSM Extract Mapping interface
Automatic Mapping
4C Supply applies simple logic to match value pairs. For instance, if the RTSM Extract contains visit numbers like ‘1, 2, 3,…’ and the specification uses ‘V1, V2, V3,…’ the system should match these automatically. This allows the system to complete the initial extract load but it will also use this logic when new values are added to the extract. The system will never update mapping values defined by the user.
Default Mapping
For values that are not commonly defined in the specification, i.e., kit status and patient status, there are default pairs applied to all studies (e.g., “Enrolled” is mapped to “Enrolled”).
Manual Mapping
In each tab, the RTSM value is displayed on the left and the 4C Supply® value is displayed on the right.
Single Value Mapping
If a single RTSM value’s mapping needs to be updated, the 4C value can simply be selected from the dropdown in the ‘Value’ column on the right hand side.
Updating mapping values
Bulk Update Mapping
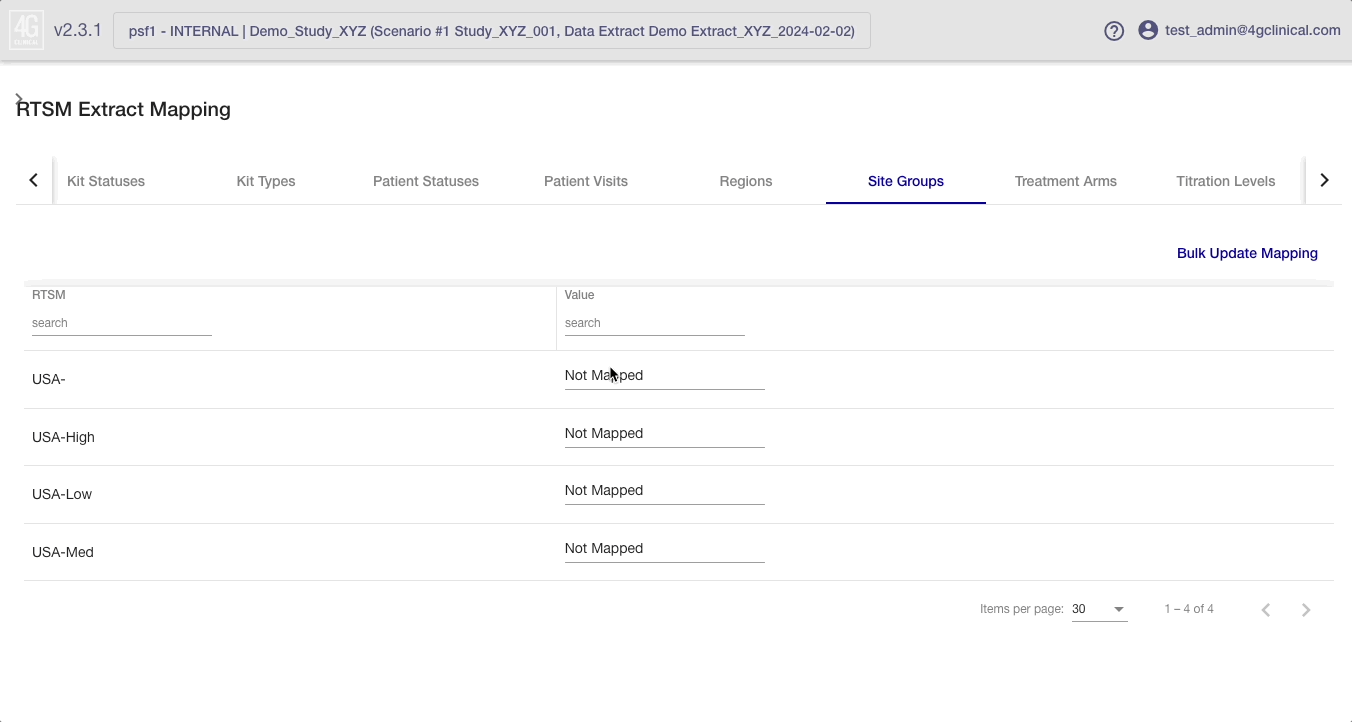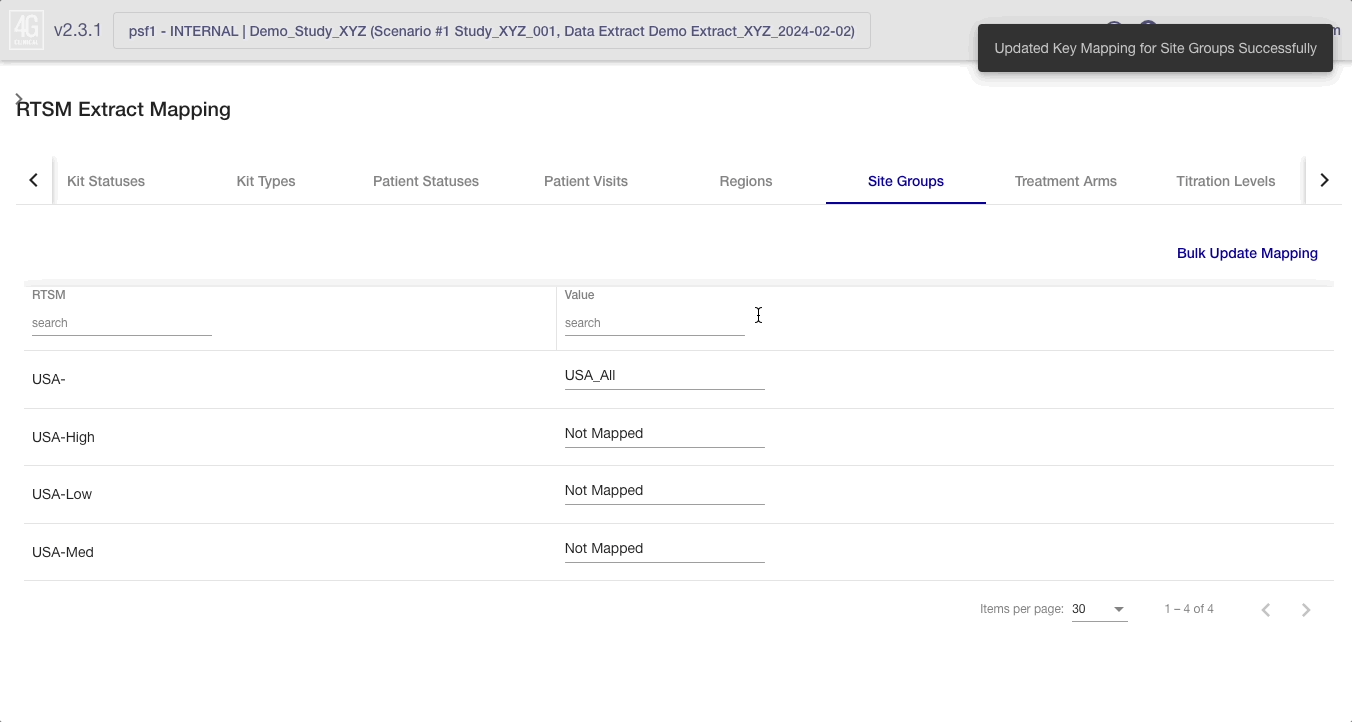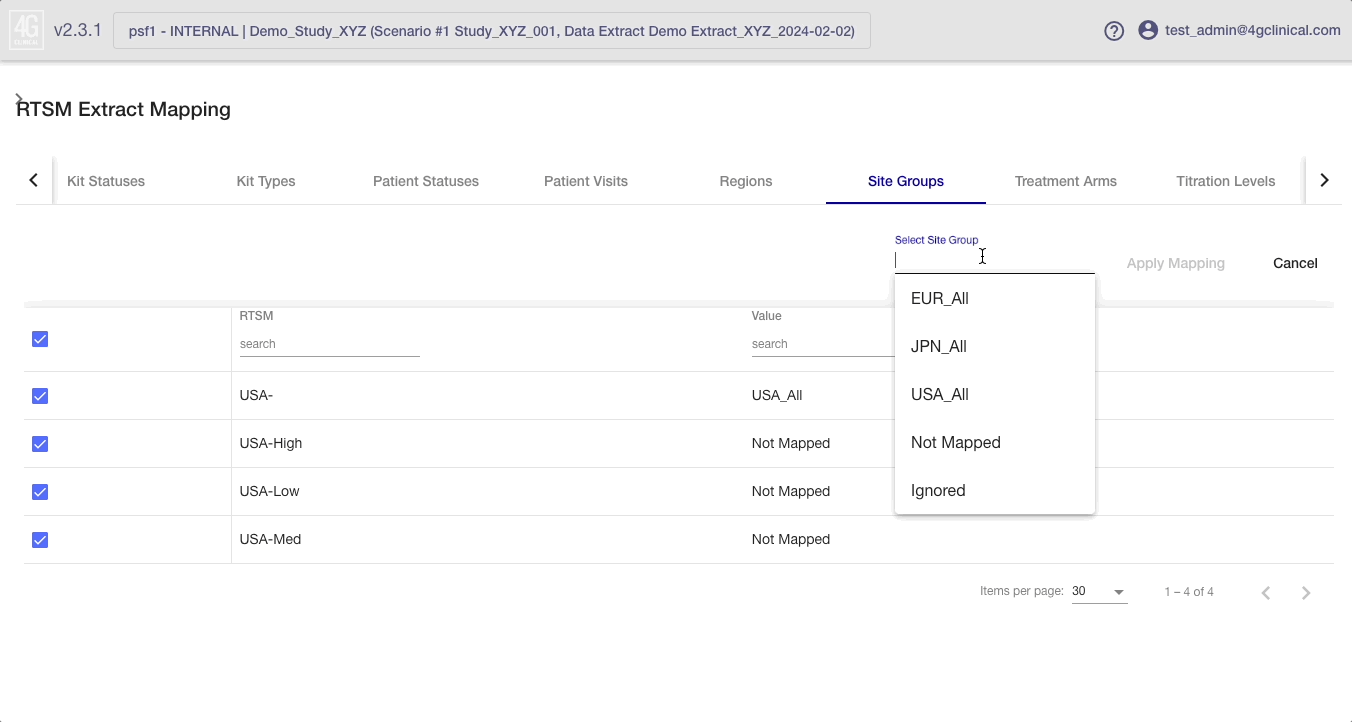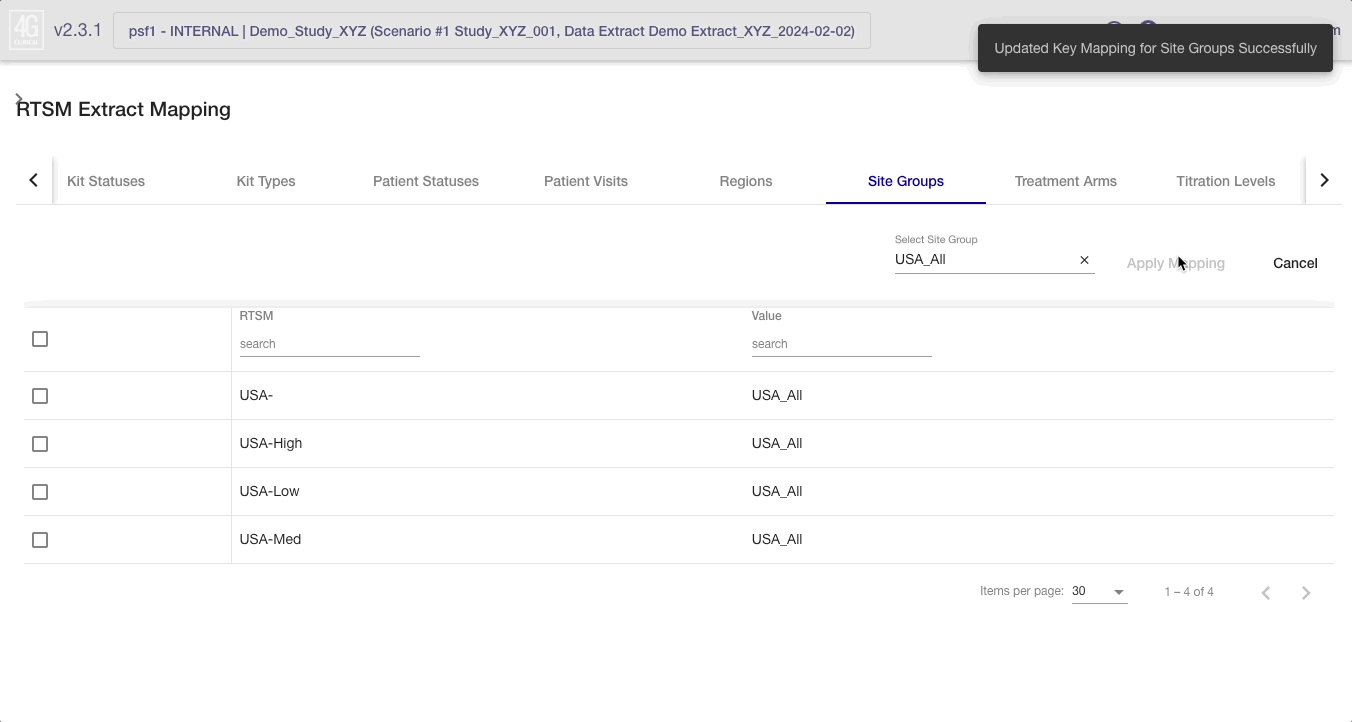
If multiple RTSM values need to be updated to a single 4C value, then the Bulk Update Mapping tool is best. Follow these steps to make a bulk change:
Clicking on the Bulk Update Mapping button will enter a selection mode.
Select the RTSM value to change using the check boxes on the left, or select all values by using the checkbox in the header bar.
Select the 4C value from the dropdown in the header bar, then select Apply Mapping.
When the system cannot automatically map an value it will show as MAPPING ERROR on the RTSM Extract Mapping page to highlight that it has not been mapped and will not be considered in the forecast. When editing these rows in the RTSM Extract Mapping they will appear blank.
Not Mapped vs. Ignored
If there is no appropriate 4C value to map to or if the value should be ignored, there are two options:
Not Mapped: Setting an RTSM value as ‘Not Mapped’ means that it will not be considered in the forecast. Updating mapping from MAPPING ERROR (default system result) to ‘Not Mapped’ will not change the outcome of the forecast.
Ignored: Setting an RTSM value as ‘Ignored' will actively drop any data connected to this value. This value and items that reference it will be ignored by the forecast.
Examples:
The RTSM Extract contains cohort information for each patient but the 4C Specification does not reference cohorts.
The mapping for cohorts can be set to Not Mapped. The patients will be included in the forecast and the unmapped value will not have any influence since the 4C specification does not reference this data.
If the mapping for a cohort is set to Ignored all patients with the ignored cohort value will be dropped from the forecast. This may be desirable if a specific cohort should not be included in the forecast.
The RTSM Extract contains cohort information for each patient and the 4C Specification also references cohorts.
The mapping for cohorts should be mapped in full to ensure no patients are lost.
A Not Mapped value will mean that the system does not know where to place the patient in relation to the visit actions tied to a cohort. If there are any visit actions that do not reference a cohort (such as screening) then patients will be recognized but only as far as this visit.
If the mapping for a cohort is set to Ignored all patients with the ignored cohort value will be dropped from the forecast.
Mapping Details
Each mapping category is described in greater detail below.
If the 4C specification is updated after the initial setup the mapping should always be updated accordingly. When mapping is updated the extract must be re-loaded to apply the changes.
If changes are made to the any values in the RTSM, corresponding changes must be made in the 4C Supply® scenario specification.
For example, if additional visits are added, dose levels are removed, or dispensing units introduced, the 4C Supply specification and mapping must be updated accordingly.
Note: It is essential that any data impacting dosing is mapped in full.
For instance, if the RTSM Extract contains Dose Level information but the 4C specification does not include it, the Dose Level information should be added to the specification so that the system can determine which path an actual patient will take through the Visit Actions table.
Similarly, if the RTSM references a dropout visit, then this must be present in the 4C specification so that the system knows to drop any patients at that visit from the forecast.
Cohorts
Displays the mapping of cohorts in the RTSM data extract to cohort codes in the 4C Supply® scenario specification. Cohorts set to ‘ignored’ will be disregarded entirely from the forecast, i.e., all actual patients that have registered that cohort will be dropped from the forecast.
Currently Enrolling Cohort
The ‘currently_enrolling_cohort’ is a data point used in all studies with cohorts, it defines what cohort patients with a ‘Screened’ status will be forecast to enroll into. It is visible in the RTSM Extract Data Export only. If the Currently Enrolling Cohort is mapped to ‘Ignored’ or ‘Not Mapped’ the forecast will fail.
Depots
Displays the mapping of depots in the RTSM data extract to depot codes in the 4C Supply® scenario specification.
Kit Statuses
Displays the mapping of kit statuses in the RTSM data extract to kit statuses in 4C Supply®.
Note: Kit statuses are not specified in the 4C Supply® scenario specification. Instead, a standard procedure is used for kit status management in 4C Supply®.
Kit Types
Displays the mapping of kit types in the RTSM data extract to dispensing unit codes in the 4C Supply® scenario specification.
Patient Statuses
Displays the mapping of patient statuses in the RTSM data extract to patient statuses in 4C Supply®.
Note: Patient statuses are not specified in the 4C Supply® scenario specification. Instead, a standard procedure is used for patient status management in 4C Supply®.
Patient Visits
Displays the mapping of patient visits in the RTSM data extract to visit codes in the 4C Supply® scenario specification.
If a visit is renamed in the RTSM, but no corresponding mapping update is made (automatically or manually), a forecast calculation error with the following message may be shown:
'NoneType' object has no attribute 'visit_date'
Regions
Displays the mapping of countries in the RTSM data extract to region codes in the 4C Supply® scenario specification.
In most RTSM systems, sites are associated with countries, while in 4C Supply® sites are associated with regions. If RTSM data extracts are used and sites are associated with countries in the RTSM, it should be specified in the 4C Supply® scenario specification that a study occurs, e.g., in regions USA, JPN, FRA, and GER rather than specifying that a study occurs in North America, Asia and Europe.
Site Groups
Displays the mapping of region/enrollment group combinations in the RTSM data extract to site groups in the 4C Supply® scenario specification. It will often make sense to map multiple enrollment groups to a single site group in 4C Supply (this is best done using the Bulk Update Mapping feature).
Treatment Arms
Displays the mapping of treatment arms in the RTSM data extract to treatment arms in the 4C Supply® scenario specification.
If visit action randomize is used to define treatment arms in the 4C Supply® scenario specification, then the mapping of treatment arms in the RTSM data extract occurs to these treatment arms.
Titration Levels
Displays the mapping of titration levels in the RTSM data extract to titration levels in the 4C Supply® scenario specification.
If visit action titration is used to define titration levels in the 4C Supply® scenario specification, then mapping of titration levels in the RTSM data extract occurs to these titration levels (dose levels).
Label Group-Lot Mapping
If a specification uses label groups, the actual lots in an RTSM extract will need to be mapped to these label groups via the Inventory Summary on the RTSM Extract Data page. All lots must be associated with a label group before a forecast can be run. If this is not done, the forecast button on the Calculation page will be non-functional and the following message will display:
“Please associate all released lots with a label group first in order to run forecast”
Custom Mapping Logic
Certain study designs and RTSM concepts (e.g. collectible data) cannot be mapped between RTSM data extracts and 4C Supply® models using the standard procedure. In some of these cases, custom logic for action mapping can be applied to achieve accurate mapping. 4G Clinical will determine when custom logic for action mapping is needed and generate the mapping script during the study setup process, contact 4csupply@4gclinical.com with the details.